- Clinical Experience
- Rheumatology
- Pulmonology
- Ophthalmology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Proposed MOA
- Dosing & Administration
- Safety Data
- Support & Resources
-
Acthar Gel is believed to work differently
Acthar Gel is a naturally sourced complex mixture of adrenocorticotropic hormone analogs and other pituitary peptides.1

AIM FOR ANOTHER WAY
Acthar Gel is thought to modulate the immune response by1-5*:
ACTIVATING
Melanocortin receptors (MCRs)
INHIBITING
Production of proinflammatory cytokines
MINIMIZING
IL-4/CD40L-stimulated activation and IgG production in human B cells
The exact mechanism of action of Acthar Gel requires further investigation. This information is based on nonclinical and pharmacodynamic data, and the relationship to clinical benefit is unknown. As shown in our package insert, it is not correct to refer to Acthar Gel simply as “ACTH” nor be considered the same or interchangeable with any other product—synthetic or natural—that may be listed as part of the ACTH class.1,6
CD40L=cluster of differentiation 40 ligand; IgG=immunoglobulin G; IL-4=interleukin 4.
*Immunomodulatory activity may vary by condition. Each modulation may not apply to all conditions.
Watch Kostas Botsoglou, MD, MPH, explain the proposed MOA of Acthar Gel
The exact mechanism of action of Acthar Gel requires further investigation. This information is based on nonclinical and pharmacodynamic data, and the relationship to clinical benefit is unknown.
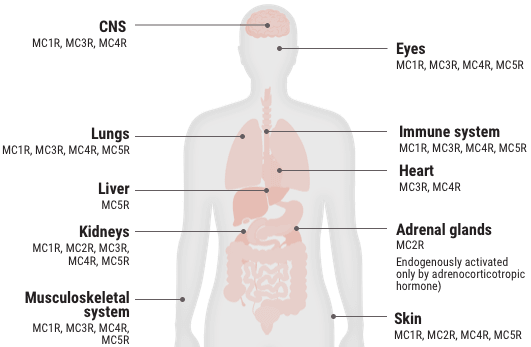
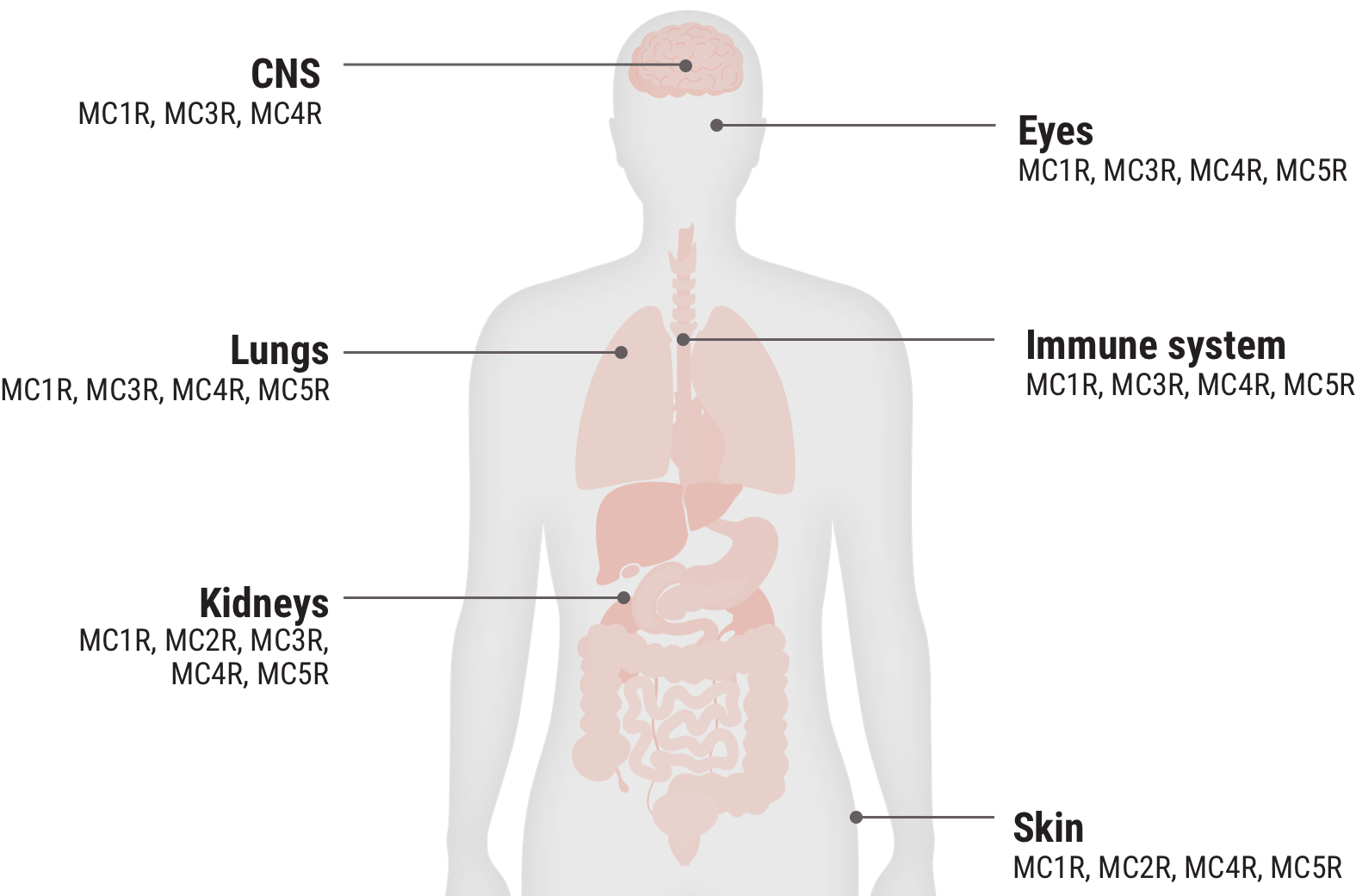
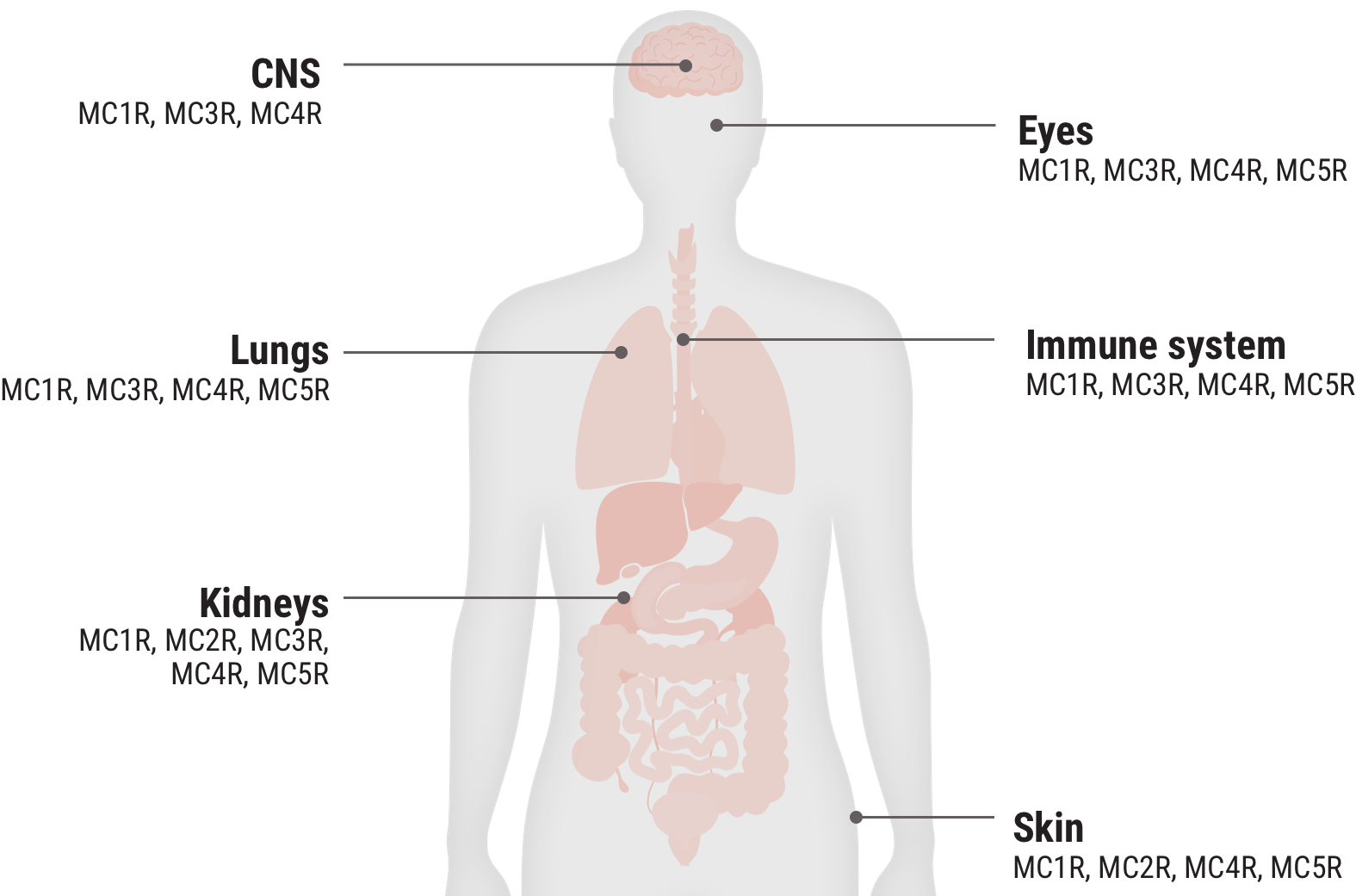
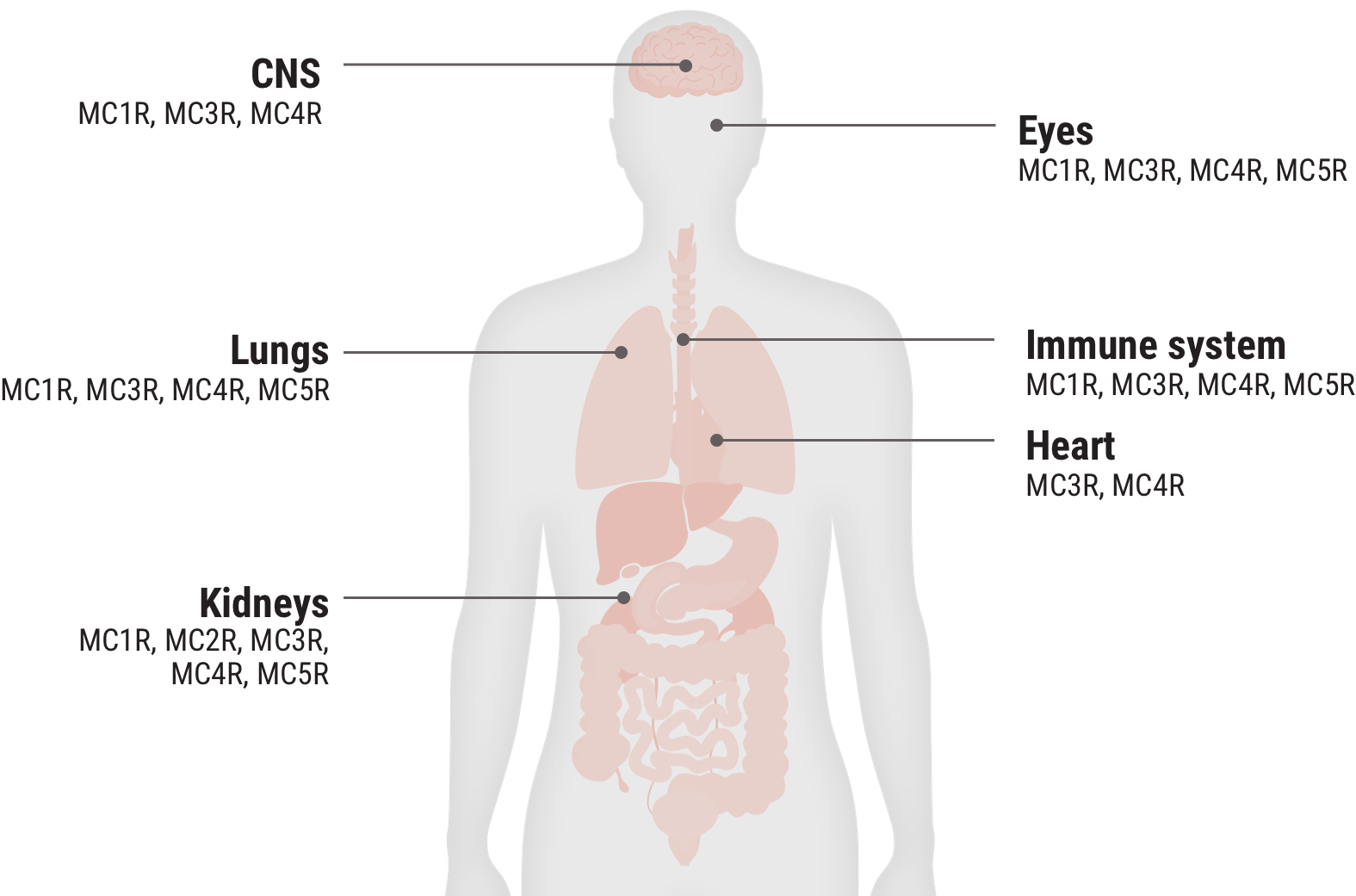
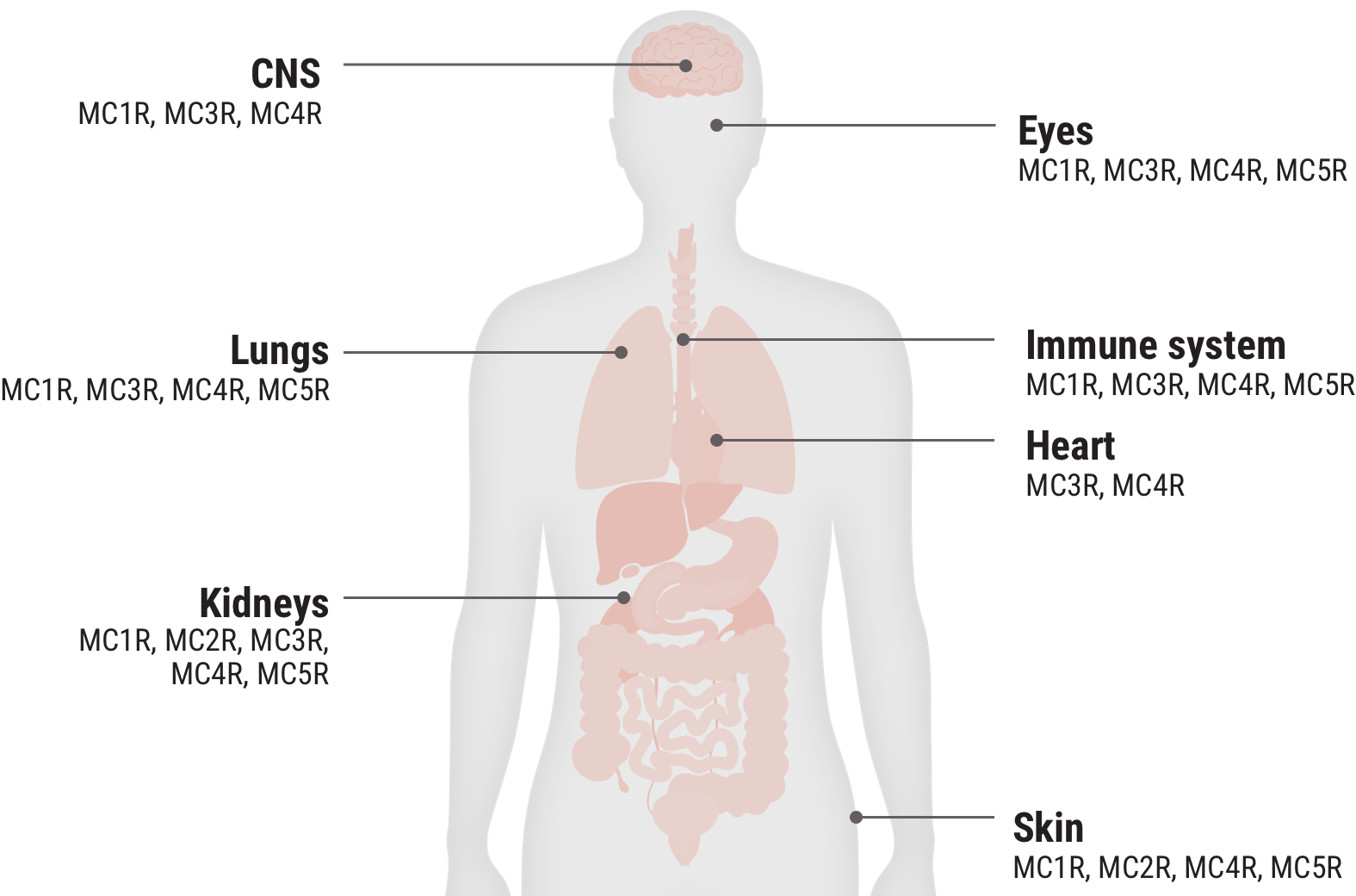
Melanocortin receptor engagement
Acthar Gel engages melanocortin receptors (MCRs) expressed on immune cells and other tissues throughout the body and is thought to produce both an indirect anti-inflammatory effect and a direct cell modulation effect2-7
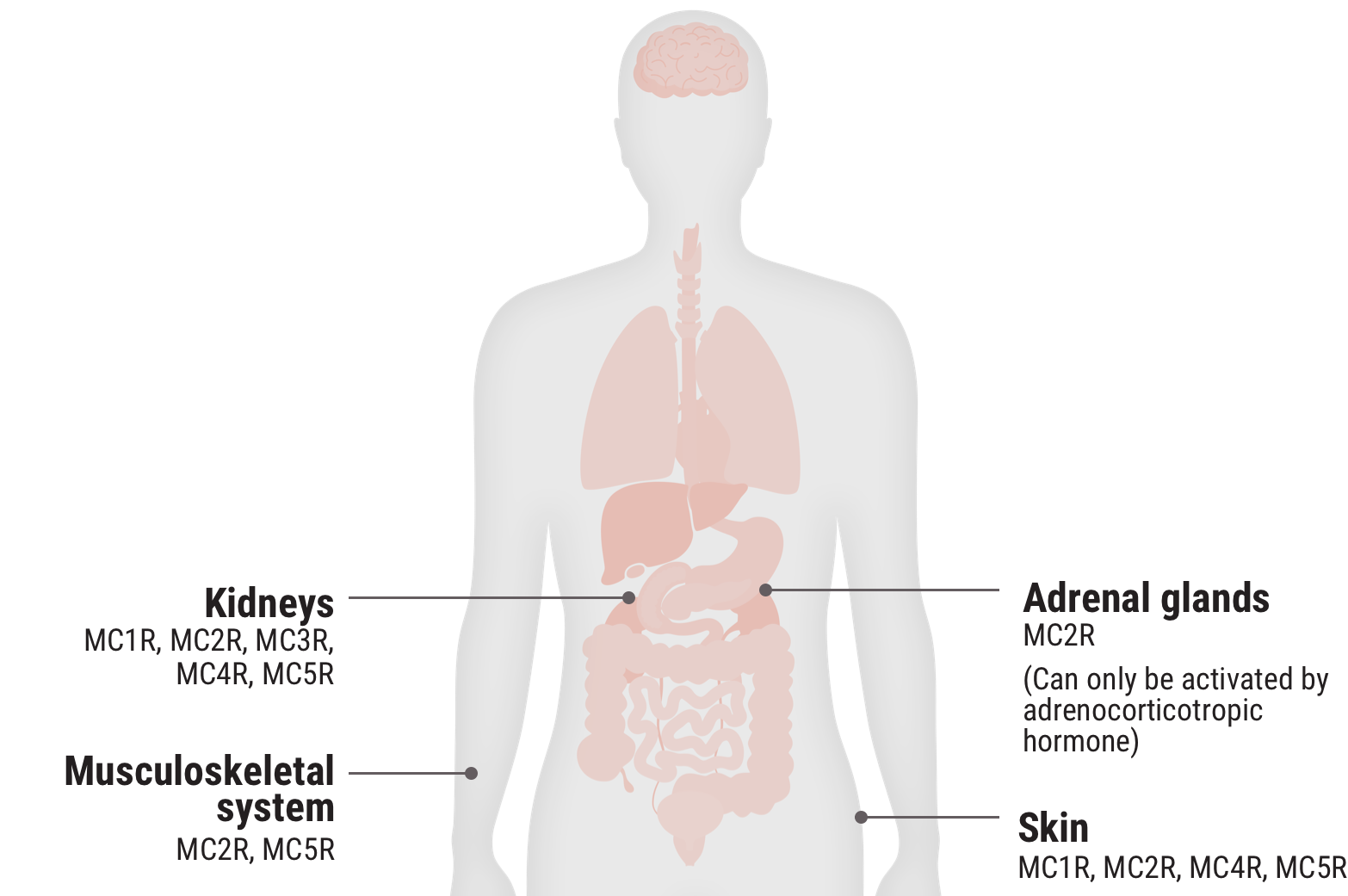
In the body, MC2Rs are primarily expressed on the adrenal cortex and the engagement of these receptors leads to the production of cortisol. The other MCRs are found on immune and other cells throughout the body. They play a key role in regulating inflammation and other cellular functions.2
In in vitro studies where the relative functional potency of MCRs was measured, 12.5% of Acthar Gel's relative functional potency occurred at MC2R. The remaining 87.5% occurred at the other MCRs.3
The exact mechanism of action of Acthar Gel requires further investigation. This information is based on nonclinical and pharmacodynamic data, and the relationship to clinical benefit is unknown.
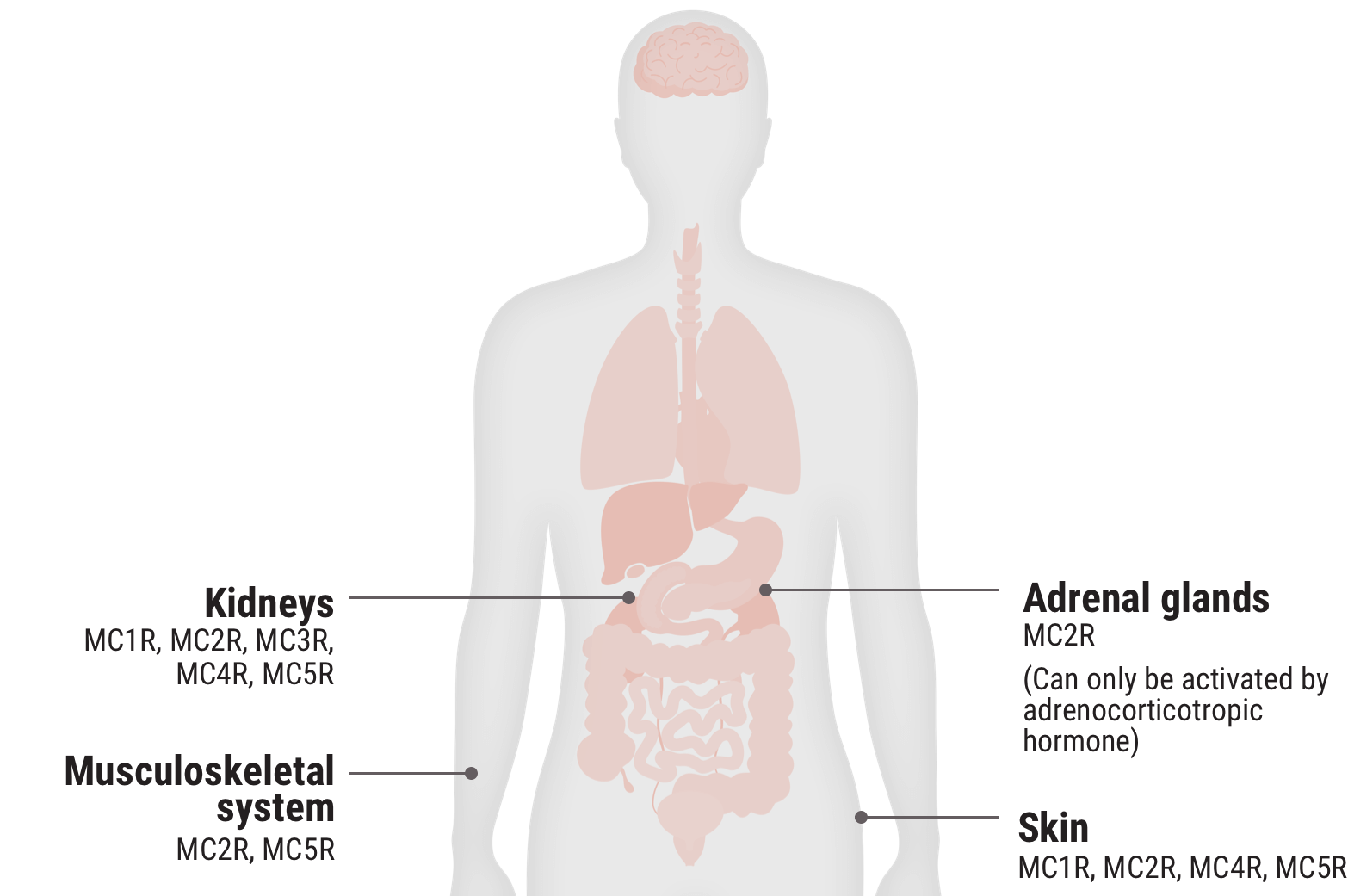
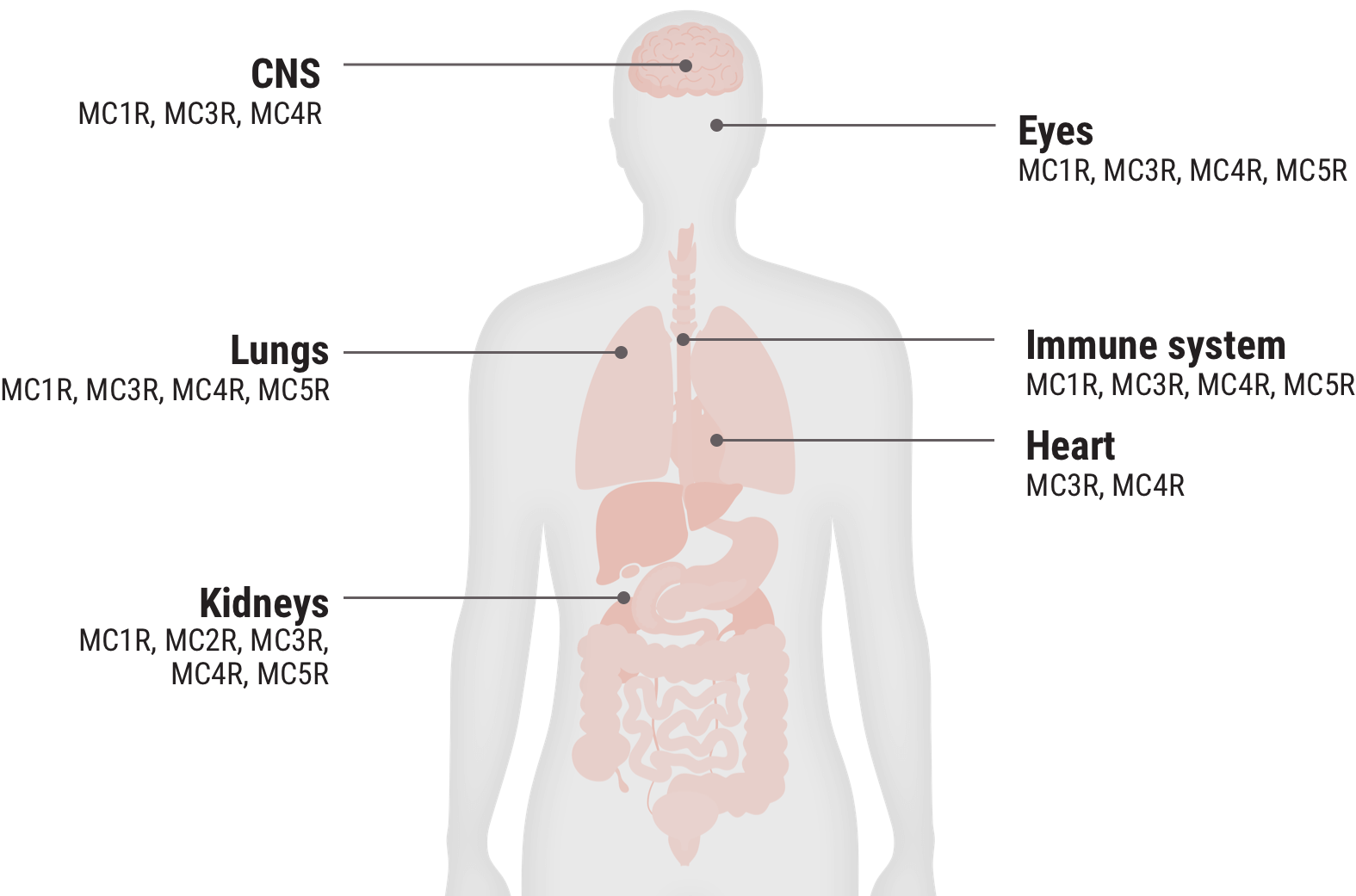
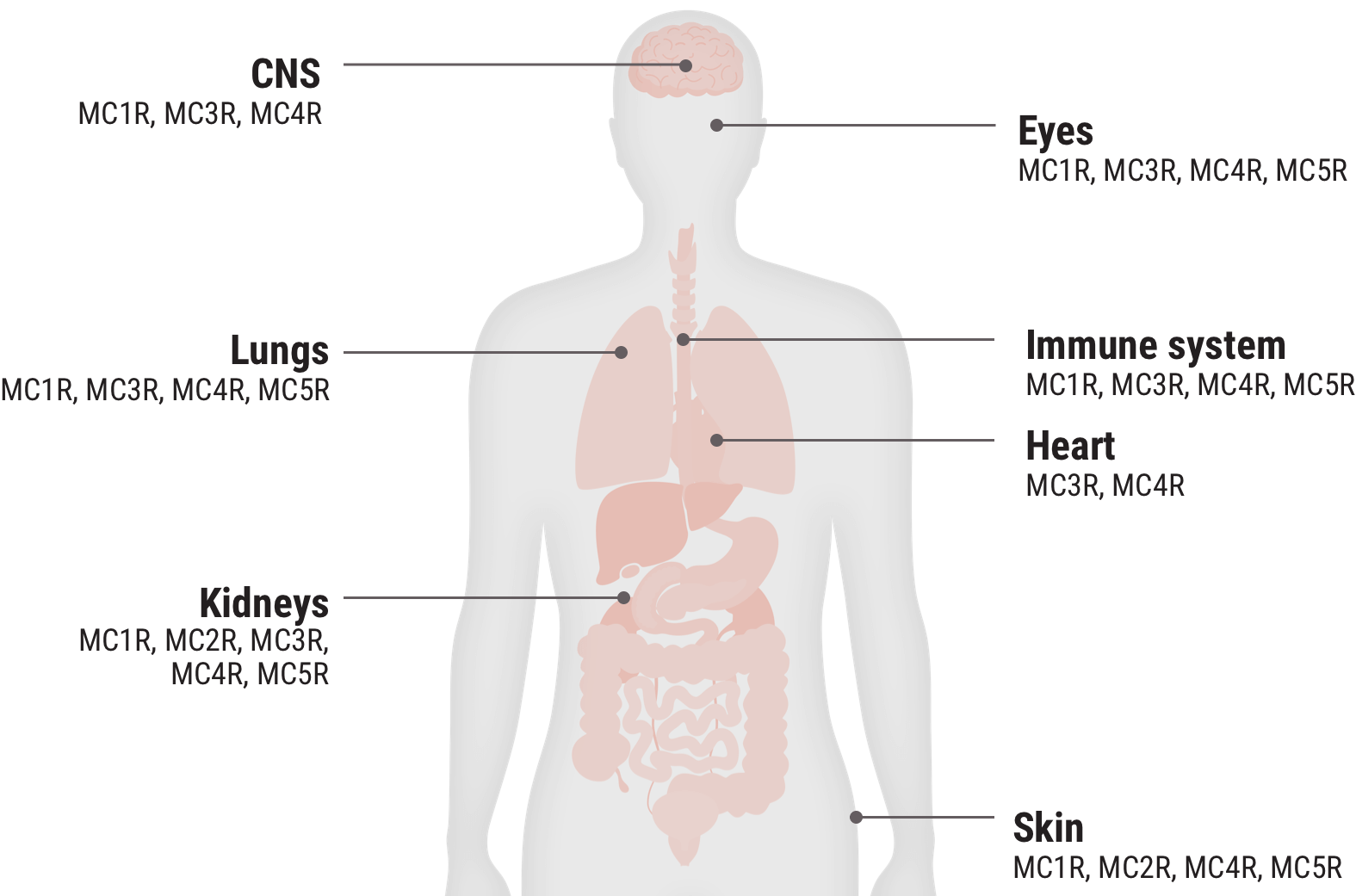
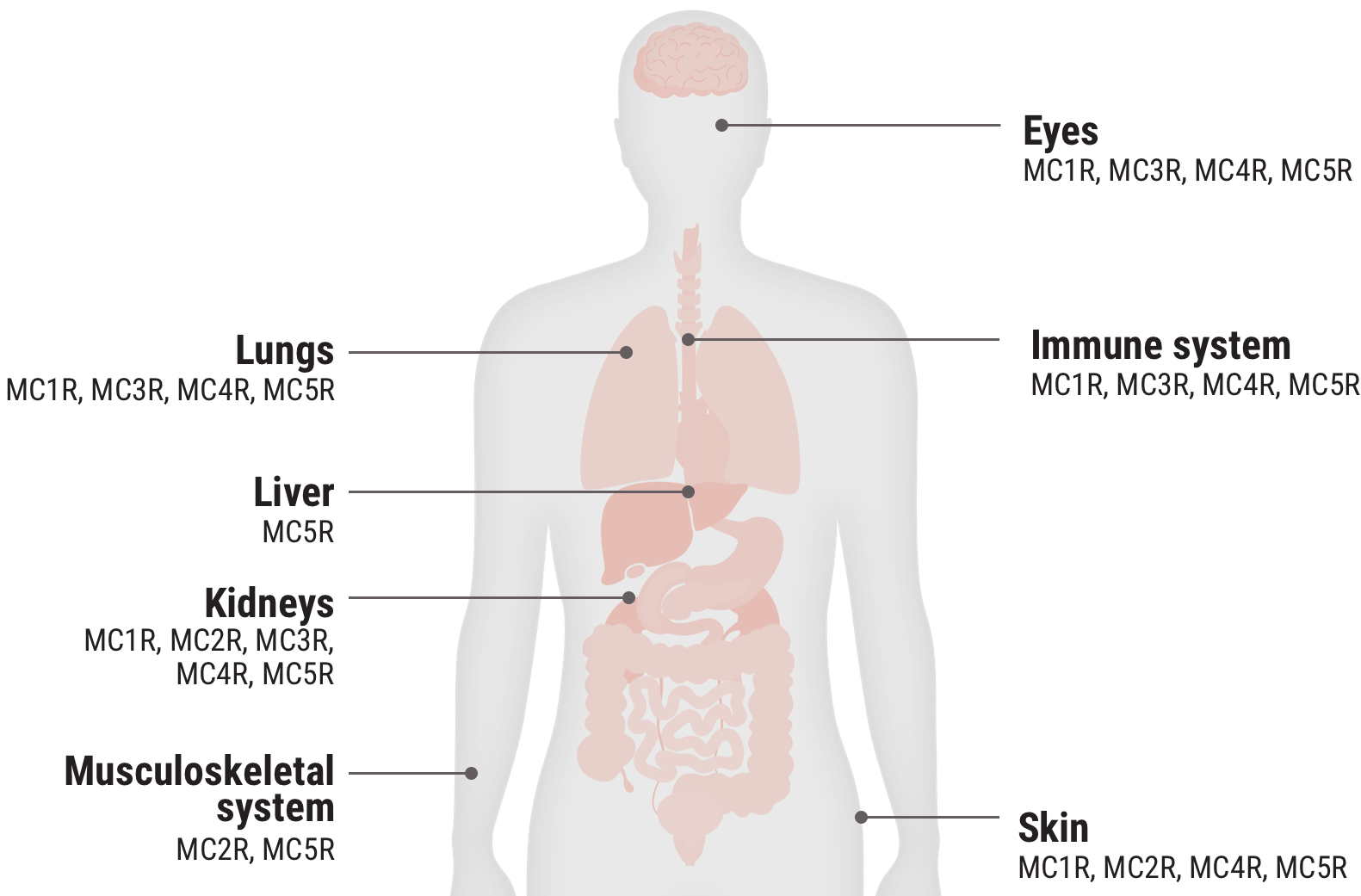
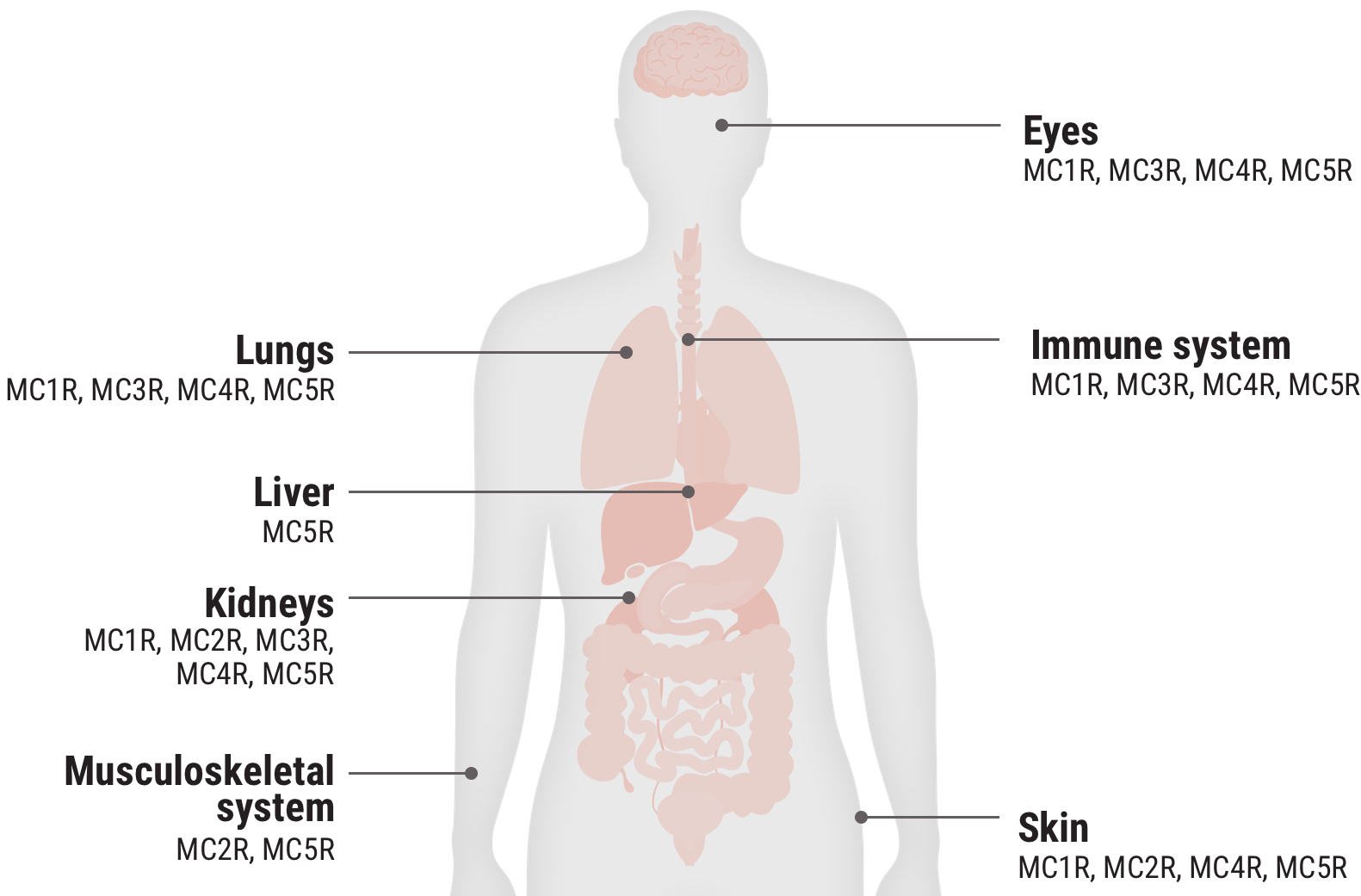
Relative functional potency of Acthar Gel at MCRs3
Select an MCR to see where it is found in the body and some associated tissues and cells.

MC1R 20.3%
MC2R 12.5%
MC3R 25.8%
MC4R 28.8%
MC5R 12.5%
- Macrophages
- Microglia
- Mast cells
- Astrocytes
- Oligodendrocytes
- Schwann cells
- Melanocytes
- Retinal pigment epithelial cells
- Bone cells
- Chondrocytes
- Podocytes
- B cells
- T cells
- Dendritic cells
- Epithelial cells
- Adipocytes
- Adrenal cortical cells
- Macrophages
- Microglia
- Oligodendrocytes
- Schwann cells
- B cells
- Chondrocytes
- Skin cells
- Retinal ganglion cells
- Microglia
- Oligodendrocyte precursor cells
- Astrocytes
- Lung tissue
- Oligodendrocytes
- Retinal ganglion cells
- B cells
- T cells
- Mast cells
- Monocytes
- Macrophages
- Microglia
- Oligodendrocytes
- Schwann cells
- Chondrocytes
- Lung tissues
- Podocytes
- Retinal pigment epithelial cells

MC1R 20.3%
Examples of cells that express MCRs2,9-17†
- Macrophages
- Microglia
- Mast cells
- Astrocytes
- Oligodendrocytes
- Schwann cells
- Melanocytes
- Retinal pigment epithelial cells
- Bone cells
- Chondrocytes
- Podocytes
- B cells
- T cells
- Dendritic cells
- Epithelial cells
†These examples are not an all-inclusive list.
MC2R 12.5%
Examples of cells that express MCRs2,9-17†;
- Adipocytes
- Adrenal cortical cells
†These examples are not an all-inclusive list.
MC3R 25.8%
Examples of cells that express MCRs2,9-17†
- Macrophages
- Microglia
- Oligodendrocytes
- Schwann cells
- B cells
- Chondrocytes
- Skin cells
- Retinal ganglion cells
†These examples are not an all-inclusive list.
MC4R 28.8%
Examples of cells that express MCRs2,9-17†
- Microglia
- Oligodendrocyte precursor cells
- Astrocytes
- Lung tissue
- Oligodendrocytes
- Retinal ganglion cells
†These examples are not an all-inclusive list.
MC5R 12.5%
Examples of cells that express MCRs2,9-17†
- B cells
- T cells
- Mast cells
- Monocytes
- Macrophages
- Microglia
- Oligodendrocytes
- Schwann cells
- Chondrocytes
- Lung tissues
- Podocytes
- Retinal pigment epithelial cells
†These examples are not an all-inclusive list.

cAMP=cyclic adenosine monophosphate; CNS=central nervous system.
*Receptor densities and the induction of cAMP are assumed to be equivalent for all receptors. Acthar Gel was observed to be a partial agonist at MC5R. Numbers may not sum to 100 due to rounding. Only results for Acthar Gel are reported above.
Study Design3
Acthar Gel was tested in vitro for its ability to increase cellular cAMP concentrations in whole cell cultures. Cell cultures expressing endogenous MC1R and MC2R, and cloned human MC3R, MC4R, and MC5R were treated with Acthar Gel. The increase in cellular cAMP concentrations was assayed. Agonist activity was determined with a minimum of 2 replicates using non-linear regression analysis of the concentration-response curves. Relative functional potency was determined by calculating the log of each EC50 value, summing EC50 values, and determining the percentage of the total for each receptor.
EC50=half maximal effective concentration.
Acthar Gel engaged MCRs on the adrenal cortex to secrete free cortisol at levels slightly above normal endogenous range2
This is thought to produce an indirect anti-inflammatory effect. Data presented are from clinically relevant doses in healthy adult subjects in pharmacodynamic studies.2
The exact mechanism of action of Acthar Gel requires further investigation. This information is based on nonclinical and pharmacodynamic data, and the relationship to clinical benefit is unknown.
Free cortisol response after a single dose
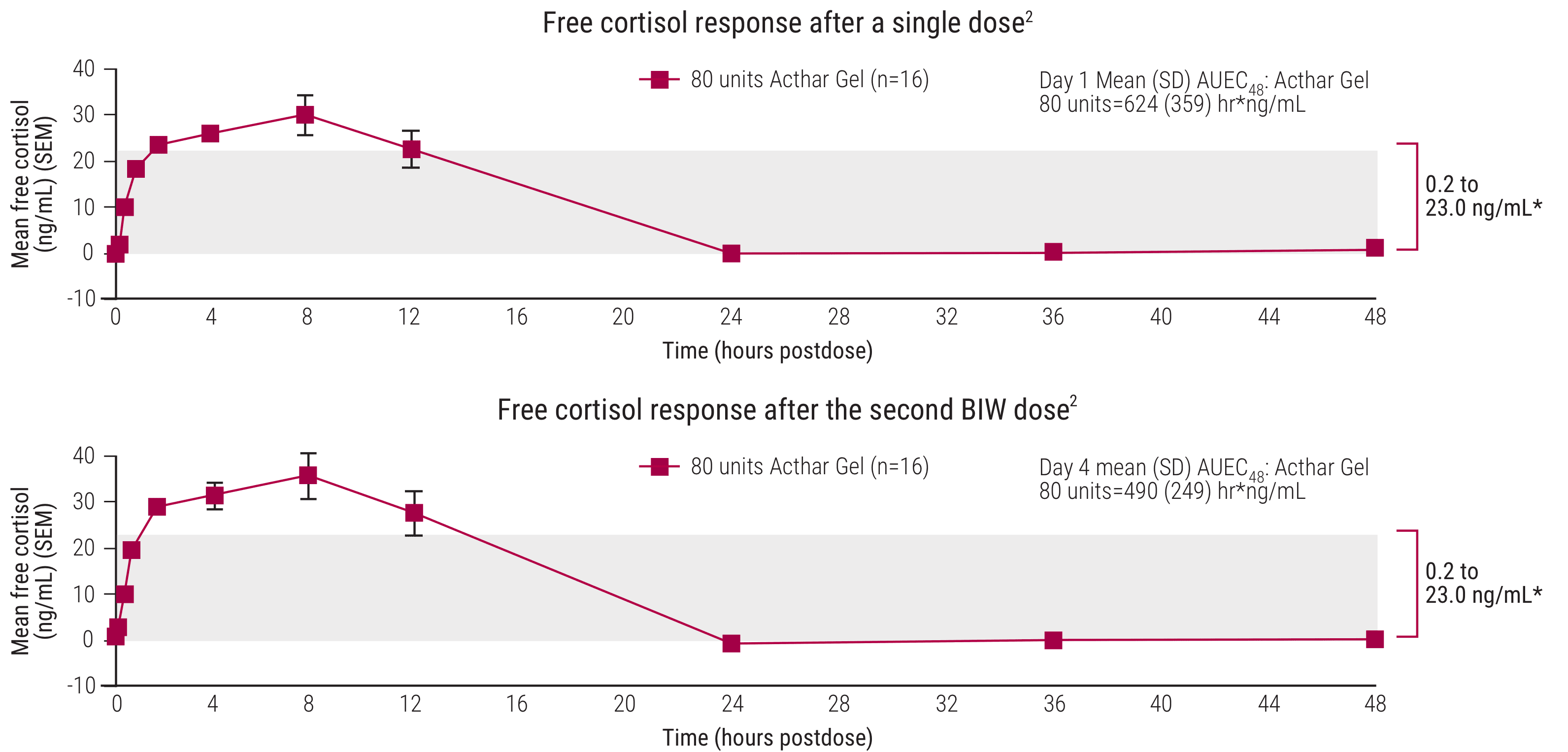
AUEC=area under the effect curve; BIW=twice weekly; SD=standard deviation; SEM=standard error of the mean.
*The baseline plasma free cortisol concentration range for all treatment groups is represented by the gray shaded area (0.2–23.0 ng/mL). Only results for Acthar Gel are reported above.
Acthar Gel 80 units dosed twice weekly in a study of healthy adults2,3:
- After 2 doses, the free cortisol exposure of Acthar Gel was equivalent to 10 mg of prednisone daily–approximately 2.5 mg above normal endogenous range
- After 5 doses, the free cortisol exposure of Acthar Gel was equivalent to 8.8 mg of prednisone daily–approximately 1.3 mg above normal endogenous range
Acthar Gel is a naturally sourced complex mixture of adrenocorticotropic hormone analogs and other pituitary peptides. Increased amounts of cortisol have the potential to increase steroidogenic side effects.1
STUDY DESIGN AND SAFETY FINDINGS
A single-center, open-label, randomized, parallel study evaluated the effects of clinically relevant doses of Acthar Gel on endogenous free cortisol production in healthy adults. An MP group was included to determine prednisone-equivalent doses. All subjects were between 18-50 years of age. Sixteen subjects received Acthar Gel 80 units SC BIW on study Days 1 and 4. Sixteen subjects received MP 32 mg PO QD for 6 days. There were 22 reported AEs in the Acthar Gel group. The most common TEAEs in the Acthar Gel group were headache and injection site reaction. Incidence of injection site reaction was 3 (18.8%) in the Acthar Gel group.
AE=adverse event; MP=methylprednisolone; PO=orally; QD=daily; SC=subcutaneous; TEAE=treatment-emergent adverse event.
Direct cell modulation
Acthar Gel has shown a direct effect on immune cell modulation2,3
In in vitro studies using human B cells, Acthar Gel significantly reduced B cell proliferation and IgG production independent of cortisol release.2,3
The exact mechanism of action of Acthar Gel requires further investigation. This information is based on nonclinical and pharmacodynamic data, and the relationship to clinical benefit is unknown.
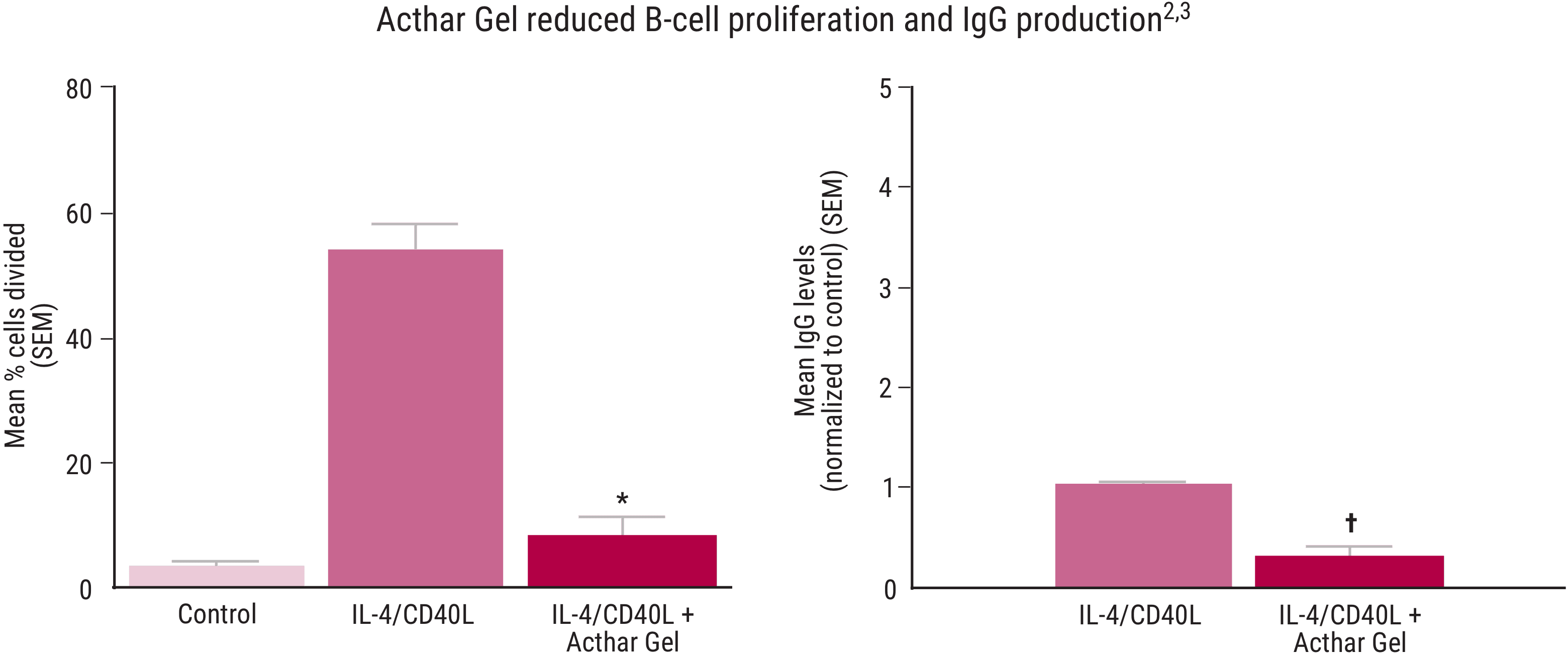
No data are available for unstimulated cells.
IgG=immunoglobulin G.
*P <.05 vs stimulated control.
†P <.0001 vs stimulated control.
Study Design2,3
The effects of Acthar Gel on human B‐lymphocyte function in vitro were evaluated using highly purified B‐cell populations cultured in the absence of glucocorticoids and stimulated by recombinant IL‐4 and CD40L as specific B‐cell activating signals. IgG was measured in supernatants from healthy human peripheral B cells cultured for 6 days. Percentage of cells that divided and IgG production were assessed following IL‐4/CD40L stimulation alone (control) or with IL‐4/CD40L plus a 1:5.5 dilution of 80 units/mL Acthar Gel. Data presented were adapted from independent studies and the highest dose tested is shown in the graphs.
CD40L=cluster of differentiation 40 ligand; IL-4=interleukin 4.
cell modulation independent of cortisol release
Acthar Gel has shown a direct effect on cytokine production from monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs)4,5
In an in vitro study using human MDMs, Acthar Gel inhibited the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α, indicating a potential anti-inflammatory effect independent of cortisol release.4,5
The exact mechanism of action of Acthar Gel requires further investigation. This information is based on nonclinical and pharmacodynamic data, and the relationship to clinical benefit is unknown.
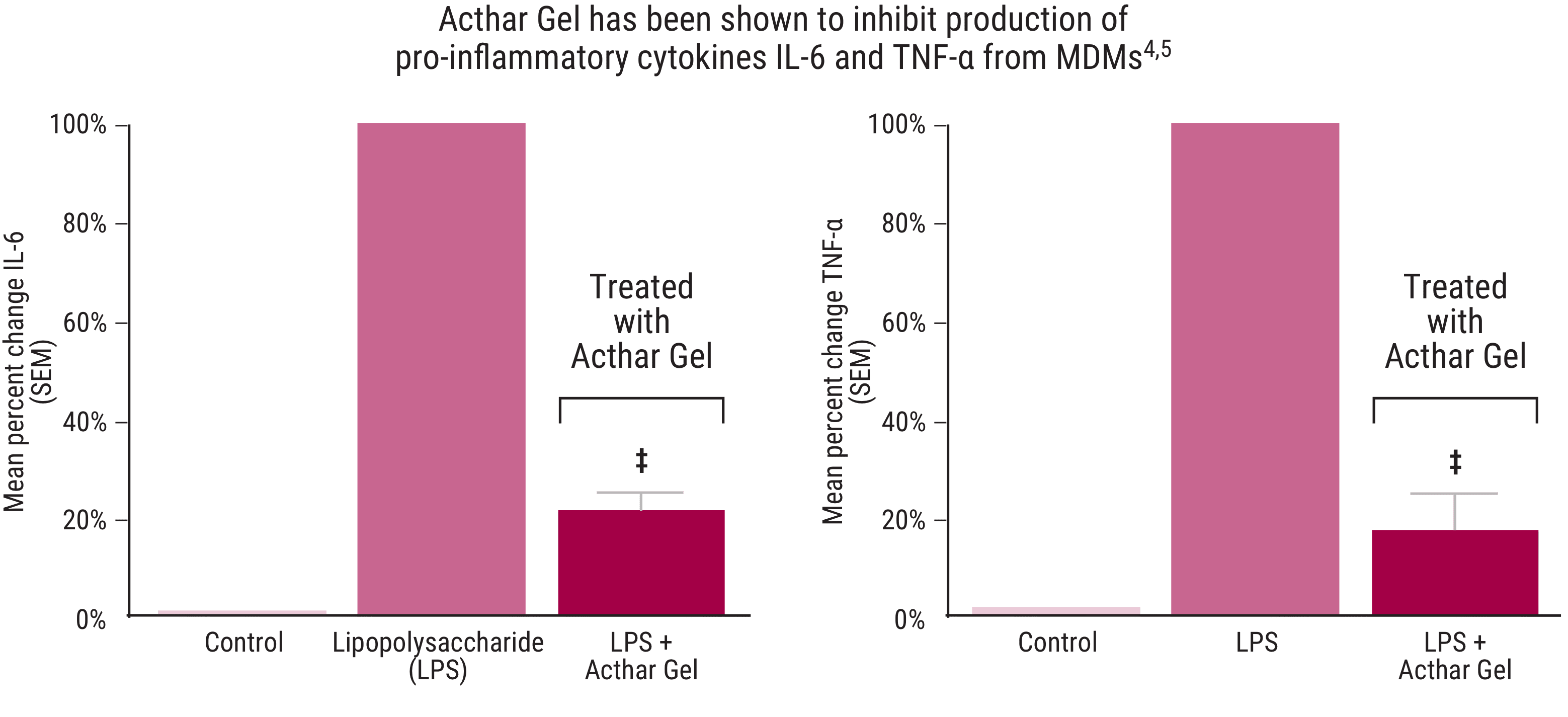
IL-6=interleukin 6; TNF-α=tumor necrosis factor α.
‡P<.0001 vs stimulated control.
Data adapted from Healy et al. 20172 are presented as percent change vs stimulated control. Only results for Acthar Gel are reported above.
Study design4,5
Acthar Gel’s direct effect on the induction of pro‐inflammatory cytokines from human macrophages following LPS stimulation was explored in an in vitro study. Human blood‐derived monocytes were selected for CD14 expression using magnetic bead selection and plated in the presence of M‐CSF. Cells were stimulated with LPS and incubated for a minimum of 24 hours with and without Acthar Gel (1:11 dilution of 80 units/mL stock). Highest dose tested is presented in graphs. Cytokines were measured with ELISA.
CD14=cluster of differentiation 14; ELISA=enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay; LPS=lipopolysaccharide; M‐CSF=macrophage colony‐stimulating factor.

Prescribe Acthar Gel now
Start the referral process for your appropriate patients

Dosing recommendations
See additional dosing information from clinical experience with Acthar Gel
INDICATIONS
Acthar Gel is indicated for:
- Treatment during an exacerbation or as maintenance therapy in selected cases of systemic dermatomyositis (polymyositis)
- Treatment during an exacerbation or as maintenance therapy in selected cases of systemic lupus erythematosus
- Adjunctive therapy for short-term administration (to tide the patient over an acute episode or exacerbation) in: psoriatic arthritis; rheumatoid arthritis, including juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (selected cases may require low-dose maintenance therapy); ankylosing spondylitis
- Symptomatic sarcoidosis
- Severe acute and chronic allergic and inflammatory processes involving the eye and its adnexa such as: keratitis, iritis, iridocyclitis, diffuse posterior uveitis and choroiditis, optic neuritis, chorioretinitis, anterior segment inflammation
- Inducing a diuresis or a remission of proteinuria in nephrotic syndrome without uremia of the idiopathic type or that due to lupus erythematosus
- Treatment of acute exacerbations of multiple sclerosis in adults. Controlled clinical trials have shown Acthar to be effective in speeding the resolution of acute exacerbations of multiple sclerosis. However, there is no evidence that it affects the ultimate outcome or natural history of the disease
- Monotherapy for the treatment of infantile spasms in infants and children under 2 years of age
Important Safety information
Contraindications
Acthar is contraindicated:
- For intravenous administration
- In infants under 2 years of age who have suspected congenital infections
- With concomitant administration of live or live attenuated vaccines in patients receiving immunosuppressive doses of Acthar
- In patients with scleroderma, osteoporosis, systemic fungal infections, ocular herpes simplex, recent surgery, history of or the presence of a peptic ulcer, congestive heart failure, uncontrolled hypertension, primary adrenocortical insufficiency, adrenocortical hyperfunction, or sensitivity to proteins of porcine origin
Warnings and Precautions
- The adverse effects of Acthar are related primarily to its steroidogenic effects
- Acthar may increase susceptibility to new infection or reactivation of latent infections
- Suppression of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis may occur following prolonged therapy with the potential for adrenal insufficiency after withdrawal of the medication. Adrenal insufficiency may be minimized by tapering of the dose when discontinuing treatment. During recovery of the adrenal gland patients should be protected from the stress (e.g., trauma or surgery) by the use of corticosteroids. Monitor patients for effects of HPA axis suppression after stopping treatment
- Cushing’s syndrome may occur during therapy but generally resolves after therapy is stopped. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms
- Acthar can cause elevation of blood pressure, salt and water retention, and hypokalemia. Monitor blood pressure and sodium and potassium levels
- Acthar often acts by masking symptoms of other diseases/disorders. Monitor patients carefully during and for a period following discontinuation of therapy
- Acthar can cause gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding and gastric ulcer. There is also an increased risk for perforation in patients with certain GI disorders. Monitor for signs of perforation and bleeding
- Acthar may be associated with central nervous system effects ranging from euphoria, insomnia, irritability, mood swings, personality changes, and severe depression to psychosis. Existing conditions may be aggravated
- Patients with comorbid disease may have that disease worsened. Caution should be used when prescribing Acthar in patients with diabetes and myasthenia gravis
- Prolonged use of Acthar may produce cataracts, glaucoma, and secondary ocular infections. Monitor for signs and symptoms
- Acthar is immunogenic and prolonged administration of Acthar may increase the risk of hypersensitivity reactions. Cases of anaphylaxis have been reported in the postmarketing setting. Neutralizing antibodies with chronic administration may lead to loss of endogenous ACTH and Acthar activity
- There may be an enhanced effect in patients with hypothyroidism and in those with cirrhosis of the liver
- Long-term use may have negative effects on growth and physical development in children. Monitor pediatric patients
- Decrease in bone density may occur. Bone density should be monitored in patients on long-term therapy
Adverse Reactions
- Commonly reported postmarketing adverse reactions for Acthar include injection site reaction, asthenic conditions (including fatigue, malaise, asthenia, and lethargy), fluid retention (including peripheral swelling), insomnia, headache, and blood glucose increased
- The most common adverse reactions for the treatment of infantile spasms (IS) are increased risk of infections, convulsions, hypertension, irritability, and pyrexia. Some patients with IS progress to other forms of seizures; IS sometimes masks these seizures, which may become visible once the clinical spasms from IS resolve
Pregnancy
- Acthar may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman
Please see full Prescribing Information for additional Important Safety Information.
References:
- Baughman RP, Barney JB, O’Hare L, Lower EE. A retrospective pilot study examining the use of Acthar Gel in sarcoidosis patients. Respir Med. 2016;110:66-72.
- Baughman RP, Sweiss N, Keijsers R, et al. Repository corticotropin for chronic pulmonary sarcoidosis. Lung. 2017;195(3):313-322.
- Madan A, Mijovic-Das S, Stankovic A, Teehan G, Milward AS, Khastgir A. Acthar Gel in the treatment of nephrotic syndrome: a multicenter retrospective case series. BMC Nephrol. 2016;17:37.
- Aggarwal R, Marder G, Koontz DC, Nandkumar P, Qi Z, Oddis CV. Efficacy and safety of adrenocorticotropic hormone gel in refractory dermatomyositis and polymyositis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(5):720-727.
- Fiechtner JJ, Montroy T. Treatment of moderately to severely active systemic lupus erythematosus with adrenocorticotropic hormone: a single-site, open-label trial. Lupus. 2014;23(9):905-912.
- Alhamad T, Dieck JM, Younus U, et al. ACTH Gel in resistant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis after kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 2019;103(1):202-209.
- Nelson WW, Lima AF, Kranyak J, et al. Retrospective medical record review to describe use of repository corticotropin injection among patients with uveitis in the United States. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2019;35(3):182-188.
- Chopra I, Qin Y, Kranyak J, et al. Repository corticotropin injection in patients with advanced symptomatic sarcoidosis: retrospective analysis of medical records. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2019;13:1-11
- Zand L, Canetta P, Lafayette R, et al. An open-label pilot study of adrenocorticotrophic hormone in the treatment of lgA nephropathy at high risk of progression. Kidney Int Rep. 2020;5(1):58-65.
- Fleischmann R, Furst DE, Connolly-Strong E, Liu J, Zhu J, Brasington R. Repository corticotropin injection for active rheumatoid arthritis despite aggressive treatment: a randomized controlled withdrawal trial. Rheumatol Ther. 2020;7(2):327-344.
- Ho-Mahler N, Turner B, Eaddy M, Hanke ML, Nelson WW. Treatment with repository corticotropin injection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and dermatomyositis/polymyositis. Open Access Rheumatol. 2020;12:21-28.
- Acthar Gel (repository corticotropin injection) [prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: Mallinckrodt ARD LLC.
- Data on File – Ref-06550. Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
- Data on File – Ref-05336. Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
- Data on File – Ref-07068. Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
- Wirta D, Mclaurin E, Ousler G, Liu J, Kacmaz RO, Grieco J. Repository corticotropin injection (Acthar® Gel) for refractory severe noninfectious keratitis: efficacy and safety from a phase 4, multicenter, open-label study. Ophthamol Ther. 2021;10(4):1077-1092.
- Tumlin J, Galphin C, Santos R, Rovin B. Kidney Int Rep. 2017;2(5):924-932.
- Grafals M, Sharfuddin A. Adrenocorticotropic hormone in the treatment of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis following kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2019;51(6):1831-1837.
- Hladunewich MA, Cattran D, Beck LH, et al. A pilot study to determine the dose and effectiveness of adrenocorticotrophic hormone (H.P. Acthar® Gel) in nephrotic syndrome due to idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2014;29(8):1570-1577.
- Filippone EJ, Dopson SJ, Rivers DM, et al. Adrenocorticotropic hormone analog use for podocytopathies. Int Med Case Rep J. 2016;9:125-133.
- Bomback AS, Tumlin JA, Baranski J, et al. Treatment of nephrotic syndrome with adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) gel. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2011;5:147-153.
- Bomback AS, Canetta PA, Beck LH Jr, Ayalon R, Radhakrishnan J, Appel GB. Treatment of resistant glomerular diseases with adrenocorticotropic hormone gel: a prospective trial. Am J Nephrol. 2012;36(1):58-67.
- Kaplan J, Miller T, Baker M, Due B, Zhao E. A prospective observational registry of repository corticotropin injection (Acthar® Gel) for the treatment of multiple sclerosis relapse. Front Neurol. 2020;11:598496.
- Bryan MS, Sergott RC. Changes in visual acuity and retinal structures following repository corticotropin injection (RCI) therapy in patients with acute demyelinating optic neuritis: improvement in low contrast visual acuity in both affected and contralateral eyes in a single-armed open-label study. J Neurol Sci. 2019;407:116505.
- Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals. Acthar® Gel (repository corticotropin injection) Reference Bibliography. https://www.mallinckrodt.com/globalassets/documents/corporate/bibliography/acthar-gel-repository-corticotropin-injection-reference-bibliography.pdf. Accessed December 7, 2023.
- Wynn D, Goldstick L, Bauer W, et al. Results from a multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of repository corticotropin injection for multiple sclerosis relapse that did not adequately respond to corticosteroids. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022;28:364-371.
- Saygin D, Oddis CV, Marder G, et al. Follow-up results of myositis patients treated with Acthar gel. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59(10):2976-2981.
- Fernandez AP, Gallop J, Polly S, Khanna U. Efficacy and safety of repository corticotropin injection for refractory cutaneous dermatomyositis: a prospective, open-label study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023 Nov 6. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead595. Epub ahead of print.
- Anesi SD, Chang PY, Maleki A, et al. Treatment of noninfectious retinal vasculitis using subcutaneous repository corticotropin injection. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2021;16(2):219-233.
- Anesi SD, Chang PY, Maleki A, et al. Effects of subcutaneous repository corticotropin gel injection on regulatory T cell population in noninfectious retinal vasculitis. Ocul Immunol lnflamm. 2023;31(3):556-565.
References:
- Acthar Gel (repository corticotropin injection) [prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: Mallinckrodt ARD LLC.
- Huang JY, Galen K, Zweifel B, Brooks LR, Wright AD. Distinct binding and signaling activity of Acthar Gel compared to other melanocortin receptor agonists. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2020;1-9. doi:10.1080/10799893.2020.1818094.
- Healy LM, Jang JH, Lin YH, Rao V, Antel JP, Wright D. Melanocortin receptor mediated anti-inflammatory effect of repository corticotropin injection on human monocyte-derived macrophages [ECTRIMS-ACTRIMS abstract EP1481]. Mult Scler J. 2017;23(suppl 3):777.
- Wright D, Hayes K. Acthar Gel inhibits the activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2023;43(4):182-187. doi: 10.1089/jir.2022.0257.
- Olsen NJ, Decker DA, Higgins P, et al. Direct effects of HP Acthar Gel on human B lymphocyte activation in vitro. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:300. doi:10.1186/s13075-015-0823-y.
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. DailyMed website. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/. Accessed March 3, 2022.
References:
- Acthar Gel (repository corticotropin injection) [prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: Mallinckrodt ARD LLC.
- Catania A, Lonati C, Sordi A, Carlin A, Leonardi P, Gatti S. The melanocortin system in control of inflammation. ScientificWorldJournal. 2010;10:1840-1853. doi:10.1100/tsw.2010.173.
- Huang YJ, Galen K, Zweifel B, Brooks LR, Wright AD. Distinct binding and signaling activity of Acthar Gel compared to other melanocortin receptor agonists. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2021;41(5):425-433.
- Olsen NJ, Decker DA, Higgins P, et al. Direct effects of HP Acthar Gel on human B lymphocyte activation in vitro. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:300. doi:10.1186/s13075-015-0823-y.
- Healy LM, Jang JH, Lin YH, Rao V, Antel JP, Wright D. Melanocortin receptor mediated anti-inflammatory effect of repository corticotropin injection on human monocyte-derived macrophages [ECTRIMS-ACTRIMS abstract EP1481]. Mult Scler J. 2017;23(suppl 3):777.
- Wright D, Hayes K. Acthar Gel inhibits the activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2023;43(4):182-187. doi: 10.1089/jir.2022.0257.
- Benko AL, McAloose CA, Becker PM, et al. Repository corticotrophin injection exerts direct acute effects on human B cell gene expression distinct from the actions of glucocorticoids. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018;192(1):68‐81.
- Gong R. The renaissance of corticotropin therapy in proteinuric nephropathies. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011;8(2):122-128.
- Caruso V, Lagerström MC, Olszewski PK, Fredriksson R, Schiöth HB. Synaptic changes induced by melanocortin signalling. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014;15(2):98‐110.
- Zhong Q, Sridhar S, Ruan L, et al. Multiple melanocortin receptors are expressed in bone cells. Bone. 2005;36(5):820‐831.
- Lisak RP, Benjamins JA. Melanocortins, melanocortin receptors and multiple sclerosis. Brain Sci. 2017;7(104):1‐18.
- Taylor AW, Lee D. Applications of the role of α‐MSH in ocular immune privilege. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;681:143‐149.
- Artuc M, Grützkau A, Luger T, Henz BM. Expression of MC1‐ and MC5‐receptors on the human mast cell line HMC‐1. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;885:364‐367.
- Chang M, Chen B, Shaffner J, Dworkin LD, Gong R. Melanocortin system in kidney homeostasis and disease: novel therapeutic opportunities. Front Physiol. 2021;12:651236.
- Lisak R, Bealmear B, Nedlekoska L, et al. Schwann cells express melanocortin receptor subtypes: activation by ACTH 1–39 and alpha‐MSH enhances proliferation [abstract P1.430]. Neurology. 2018;90(suppl 15):1‐2.
- Kaneva MK, Kerrigan MJ, Grieco P, Curley GP, Locke IC, Getting SJ. Chondroprotective and anti‐inflammatory role of melanocortin peptides in TNF‐α activated human C‐20/A4 chondrocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 2012;167(1):67‐79.
- Grässel S, Opolka A, Anders S, et al. The melanocortin system in articular chondrocytes: melanocortin receptors, pro‐opiomelanocortin, precursor proteases, and a regulatory effect of alpha‐melanocyte‐stimulating hormone on proinflammatory cytokines and extracellular matrix components. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(10):3017‐3027.
References:
- Acthar Gel (repository corticotropin injection) [prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: Mallinckrodt ARD LLC.
- Poola N, Due B, Wright D, Brooks LR, Zaman F. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of repository corticotropin injection compared with synthetic ACTH1-24 depot and methylprednisolone in healthy subjects [published online ahead of print]. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2021. doi:10.1002/cpdd.1020.
- Data on file: REF-03003. Mallinckrodt ARD LLC.
References:
- Acthar Gel (repository corticotropin injection) [prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: Mallinckrodt ARD LLC.
- Olsen NJ, Decker DA, Higgins P, et al. Direct effects of HP Acthar Gel on human B-lymphocyte activation in vitro. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:300.
- Data on file: REF-04768. Mallinckrodt ARD LLC
- Healy LM, Jang JH, Lin YH, Rao V, Antel JP, Wright D. Melanocortin receptor mediated anti-inflammatory effect of repository corticotropin injection on human monocyte-derived macrophages [ECTRIMS-ACTRIMS abstract EP14841]. Mult Scler J. 2017;23(suppl 3):777.
- Healy LM, Lin YH, Jang JH, Rao V, Antel JP, Wright D. Melanocortin receptor mediated anti-inflammatory effect of repository corticotropin injection on human monocyte-derived macrophages. Poster presented at: 7th Joint ECTRIMS-ACTRIMS Meeting; October 25-28, 2017; Paris, France. Poster EP1481.
References:
- Acthar Gel (repository corticotropin injection) [prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: Mallinckrodt ARD LLC.
- Aggarwal R, Marder G, Koontz DC, Nandkumar P, Qi Z, Oddis CV. Efficacy and safety of adrenocorticotropic hormone gel in refractory dermatomyositis and polymyositis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(5):720-727.
- Fiechtner JJ, Montroy T. Treatment of moderately to severely active systemic lupus erythematosus with adrenocorticotropic hormone: a single-site, open-label trial. Lupus. 2014;23(9):905-912.
- Fleischmann R, Furst DE, Connolly-Strong E, Liu J, Zhu J, Brasington R. Repository corticotropin injection for active rheumatoid arthritis despite aggressive treatment: a randomized controlled withdrawal trial. Rheumatol Ther. 2020;7(2):327-344.
- Fiechtner JJ, Montroy T, June J. A single-site, investigator initiated open-label trial of H.P. Acthar® Gel (repository corticotropin injection) an adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) analogue in subjects with moderately to severely active psoriatic arthritis (PsA). J Dermatol Res Ther. 2016;2(5):1-7.
- Baughman RP, Sweiss N, Keijsers R, et al. Repository corticotropin for chronic pulmonary sarcoidosis. Lung. 2017;195(3):313-322.
- Zand L, Canetta P, Lafayette R, et al. An open-label pilot study of adrenocorticotrophic hormone in the treatment of IgA nephropathy at high risk of progression. Kidney Int Rep. 2020;5(1):58-65.
- Wirta D, McLaurin E, Ousler G, Liu J, Kacmaz RO, Grieco J. Repository corticotropin injection (Acthar® Gel) for refractory severe noninfectious keratitis: efficacy and safety from a phase 4, multicenter, open-label study. Ophthalmol Ther. 2021;10(4):1077-1092.
- Anesi SD, Chang PY, Maleki A, et al. Treatment of noninfectious retinal vasculitis using subcutaneous repository corticotropin injection. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2021;16(2):219-233.
- Bryan MS, Sergott RC. Changes in visual acuity and retinal structures following repository corticotropin injection (RCI) therapy in patients with acute demyelinating optic neuritis: improvement in low contrast visual acuity in both affected and contralateral eyes in a single-armed open-label study. J Neurol Sci. 2019;407:116505.
- Wynn D, Goldstick L, Bauer W, et al. Results from a multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of repository corticotropin injection for multiple sclerosis relapse that did not adequately respond to corticosteroids. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022;28:364-371.
References:
- Acthar Gel (repository corticotropin injection) [prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: Mallinckrodt ARD LLC.
- Acthar Gel (repository corticotropin injection) Single-Dose Pre-filled SelfJect Injector, 40 USP Units/0.5 mL [Instructions for Use]. Bridgewater, NJ: Mallinckrodt ARD LLC.
- Acthar Gel (repository corticotropin injection) Single-Dose Pre-filled SelfJect Injector, 80 USP Units/1.0 mL [Instructions for Use]. Bridgewater, NJ: Mallinckrodt ARD LLC.
- Data on File — Ref-07341. Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
References:
- Acthar Gel (repository corticotropin injection) [prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: Mallinckrodt ARD LLC.
- Kaplan J, Askanase A, Chu D, et al. Acthar® Gel treatment for patients with autoimmune and inflammatory diseases: an historical perspective and characterization of clinical evidence. Clin Drug Invest. 2023;43:739-761.
- Saygin D, Oddis CV, Marder G, et al. Follow-up results of myositis patients treated with Acthar gel. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59(10):2976-2981.
- Fleischmann R, Furst DE, Connolly-Strong E, Liu J, Zhu J, Brasington R. Repository corticotropin injection for active rheumatoid arthritis despite aggressive treatment: a randomized controlled withdrawal trial. Rheumatol Ther. 2020;7(2):327-344.
- Chopra I, Qin Y, Kranyak J, et al. Repository corticotropin injection in patients with advanced symptomatic sarcoidosis: retrospective analysis of medical records. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2019;13:1-11.
- Baughman RP, Barney JB, O'Hare L, Lower EE. A retrospective pilot study examining the use of Acthar Gel in sarcoidosis patients. Respir Med. 2016;110:66-72.
- Zand L, Canetta P, Lafayette R, et al. An open-label pilot study of adrenocorticotrophic hormone in the treatment of lgA nephropathy at high risk of progression. Kidney Int Rep. 2020;5(1):58·65.
- Alhamad T, Manllo Dieck J, Younus U, et al. ACTH gel in resistant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis after kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 2019;103(1):202-209.
- Nelson WW, Lima AF, Kranyak J, et al. Retrospective medical record review to describe use of repository corticotropin injection among patients with uveitis in the United States. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2019;35(3):182-188.
- Kaplan J, Miller T, Baker M, Due B, Zhao E. A prospective observational registry of repository corticotropin injection (Acthar® Gel) for the treatment of multiple sclerosis relapse. Front Neurol. 2020;11:598496.
- Bryan MS, Sergott RC. Changes in visual acuity and retinal structures following repository corticotropin injection (RCI) therapy in patients with acute demyelinating optic neuritis: improvement in low contrast visual acuity in both affected and contralateral eyes in a single-armed open-label study. J Neurol Sci. 2019;407:116505.
- Aggarwal R, Marder G, Koontz DC, Nandkumar P, Qi Z, Oddis CV. Efficacy and safety of adrenocorticotropic hormone gel in refractory dermatomyositis and polymyositis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(5):720-727.
- Baughman RP, Sweiss N, Keijsers R, et al. Repository corticotropin for chronic pulmonary sarcoidosis. Lung. 2017;195(3):313-322.
References:
- Fleischmann R, Furst DE, Connolly-Strong E, Liu J, Zhu J, Brasington R. Repository corticotropin injection for active rheumatoid arthritis despite aggressive treatment: a randomized controlled withdrawal trial. Rheumatol Ther. 2020;7(2):327-344.
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Enrichment strategies for clinical trials to support determination of effectiveness of human drugs and biological products. Guidance for industry. March 2019. https://www.fda.gov/media/121320/download. Accessed June 11, 2019.
- Fleischmann R, Furst DE, Connolly-Strong E, Liu J, Zhu J, Brasington R. A multicenter study assessing the efficacy and safety of repository corticotropin injection in patients with persistently active rheumatoid arthritis. Poster presented at: European Congress of Rheumatology; June 12-15, 2019; Madrid, Spain.
- Curtis JR, Yang S, Chen L, et al. Determining the minimally important difference in the clinical disease activity index for improvement and worsening in early rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2015;67(10):1345-1353.
- Orbai AM, Bingham CO III. Patient reported outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2015;17(4):28.
References:
- Ho-Mahler N, Turner B, Eaddy M, Hanke ML, Nelson WW. Treatment with repository corticotropin injection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and dermatomyositis/polymyositis. Open Access Rheumatol. 2020;12:21-28.
- Acthar Gel (repository corticotropin injection) [prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: Mallinckrodt ARD LLC.
References:
- Aggarwal R, Marder G, Koontz DC, Nandkumar P, Qi Z, Oddis CV. Efficacy and safety of adrenocorticotropic hormone gel in refractory dermatomyositis and polymyositis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(5):720-727.
- National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences. Disease activity core set measures. https://www.niehs.nih.gov/research/resources/imacs/diseaseactivity/index.cfm. Updated August 31, 2017. Accessed October 10, 2022.
References:
- Saygin D, Oddis CV, Marder G, et al. Follow-up results of myositis patients treated with Acthar gel. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59(10):2976-2981.
References:
- Fiechtner JJ, Montroy T. Treatment of moderately to severely active systemic lupus erythematosus with adrenocorticotropic hormone: a single-site, open-label trial. Lupus. 2014;23(9):905-912.
References:
- Kaplan J, Miller T, Baker M, Due B, Zhao E. A prospective observational registry of repository corticotropin injection (Acthar® Gel) for the treatment of multiple sclerosis relapse. Front Neurol. 2020;11:598496.doi:10.3389/fneur.2020.598496.
- Polman CH, Reingold SC, Banwell B, et al. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald Criteria. Ann Neurol. 2011;69(2):292-302.
- Hobart J, Lamping D, Fitzpatrick R, Riazi A, Thompson A. The Multiple Sclerosis Impact Scale (MSIS-29): a new patient-based outcome measure. Brain. 2001;124(pt 5):962-973.
- Jones KH, Ford DV, Jones PA, et al. The physical and psychological impact of multiple sclerosis using the MSIS-29 via the web portal of the UK MS Register. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e5542. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0055422.
- Costelloe L, O'Rourke K, Kearney H, et al. The patient knows best: significant change in the physical component of the Multiple Sclerosis Impact Scale (MSIS-29 physical). J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007;78(8):841-844.
- Widener GL, Allen DD. Measurement characteristics and clinical utility of the 29-item Multiple Sclerosis Impact Scale. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014;95(3):593-594.
- Kurtzke JF. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology. 1983;33(11):1444-1452.
- Busner J, Targum SD. The clinical global impressions scale: applying a research tool in clinical practice. Psychiatry (Edgmont). 2007;4(7):28-37.
- Acthar Gel (repository corticotropin injection) [prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: Mallinckrodt ARD LLC.
References:
- Bryan MS, Sergott RC. Changes in visual acuity and retinal structures following repository corticotropin injection (RCI) therapy in patients with acute demyelinating optic neuritis: improvement in low contrast visual acuity in both affected and contralateral eyes in a single-armed open-label study. J Neurol Sci. 2019;407:116505. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2019.116505.
References:
- Knupp KG, Coryell J, Nickels KC, et al. Response to treatment in a prospective national infantile spasms cohort. Ann Neurol. 2016;79(3):475-484.
References:
- Madan A, Mijovic-Das S, Stankovic A, Teehan G, Milward AS, Khastgir A. Acthar gel in the treatment of nephrotic syndrome: a multicenter retrospective case series. BMC Nephrol. 2016;17(1):37. doi:10.1186/s12882-016-0241-7.
- Data on File – Ref-00742. Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Glomerulonephritis Work Group. Clinical practice guideline for glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;2(2):139-274.
References:
- Baughman RP, Barney JB, O'Hare L, Lower EE. A retrospective pilot study examining the use of Acthar gel in sarcoidosis patients. Respir Med. 2016;110:66-72.
References:
- Baughman RP, Sweiss N, Keijsers R, et al. Repository corticotropin for chronic pulmonary sarcoidosis. Lung. 2017;195(3):313-322.
References:
- Data on File – Ref-05336. Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
- Data on File – Ref-05814. Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
- Fleischmann R, Furst DE, Connolly-Strong E, Liu J, Zhu J, Brasington R. Repository corticotropin injection for active rheumatoid arthritis despite aggressive treatment: a randomized controlled withdrawal trial. Rheumatol Ther. 2020;7(2):327-344.
- Chopra I, Qin Y, Kranyak J, et al. Repository corticotropin injection in patients with advanced symptomatic sarcoidosis: retrospective analysis of medical records. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2019;13:1753466619888127. doi:10.1177/1753466619888127.
- Wirta D, McLaurin E, Ousler G, Liu J, Kacmaz RO, Grieco J. Repository corticotropin injection (Acthar® Gel) for refractory severe noninfectious keratitis: efficacy and safety from a phase 4, multicenter, open-label study. Ophthalmol Ther. 2021;10(4):1077-1092.
- Zand L, Canetta P, Lafayette R, et al. An open-label pilot study of adrenocorticotrophic hormone in the treatment of IgA nephropathy at high risk of progression. Kidney Int Rep. 2020;5(1):58-65.
- Kaplan J, Miller T, Baker M, Due B, Zhao E. A prospective observational registry of repository corticotropin injection (Acthar® Gel) for the treatment of multiple sclerosis relapse. Front Neurol. 2020;11:598496.doi:10.3389/fneur.2020.598496.
References:
- Alhamad T, Manllo Dieck J, Younus U, et al. ACTH gel in resistant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis after kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 2019;103(1):202-209.
- Acthar Gel (repository corticotropin injection) [prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: Mallinckrodt ARD LLC.
- Hladunewich MA, Cattran D, Beck LH, et al. A pilot study to determine the dose and effectiveness of adrenocorticotrophic hormone (Acthar® Gel) in nephrotic syndrome due to idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2014;29(8):1570-1577.
- Bomback AS, Canetta PA, Beck LH Jr, Ayalon R, Radhakrishnan J, Appel GB. Treatment of resistant glomerular diseases with adrenocorticotropic hormone gel: a prospective trial. Am J Nephrol. 2012;36(1):58-67.
- Madan A, Mijovic-Das S, Stankovic A, Teehan G, Milward AS, Khastgir A. Acthar Gel in the treatment of nephrotic syndrome: a multicenter retrospective case series. BMC Nephrol. 2016;17:37.
- Tumlin J, Galphin C, Santos R, Rovin B. Kidney Int Rep. 2017;2(5):924-932.
- Bomback AS, Tumlin JA, Baranski J, et al. Treatment of nephrotic syndrome with adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) gel. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2011;5:147-153.
- Filippone EJ, Dopson SJ, Rivers DM, et al. Adrenocorticotropic hormone analog use for podocytopathies. Int Med Case Rep J. 2016;9:125-133.
- Hogan J, Bomback AS, Mehta K, et al. Treatment of idiopathic FSGS with adrenocorticotropic hormone gel. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013;8(12):2072-2081.
References:
- Zand L, Canetta P, Lafayette R, et al. An open-label pilot study of adrenocorticotrophic hormone in the treatment of lgA nephropathy at high risk of progression. Kidney Int Rep. 2020;5(1):58-65.
References:
- Baram TZ, Mitchell WG, Tournay A, Snead OC, Hanson RA, Horton EJ. High-dose corticotropin (ACTH) versus prednisone for infantile spasms: a prospective, randomized, blinded study. Pediatrics. 1996;97(3):375-379.
- Acthar Gel (repository corticotropin injection) [prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: Mallinckrodt ARD LLC.
References:
- Data on file: REF-MNK14084113. Mallinckrodt ARD LLC.
References:
- Bryan MS, Sergott RC. Changes in visual acuity and retinal structures following repository corticotropin injection (RCI) therapy in patients with acute demyelinating optic neuritis: improvement in low contrast visual acuity in both affected and contralateral eyes in a single-armed open-label study. J Neurol Sci. 2019;407:116505. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2019.116505.
References:
- Fiechtner JJ, Montroy T, June J. A single-site, investigator initiated open-label trial of H.P. Acthar® Gel (repository corticotropin injection) an adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) analogue in subjects with moderately to severely active psoriatic arthritis (PsA). J Dermatol Res Ther. 2016;2(5):1-7.
- Schmitt J, Wozel G. The psoriasis area and severity index is the adequate criterion to define severity in chronic plaque-type psoriasis. Dermatology. 2005;210(3):194-199.
References:
- Chopra I, Qin Y, Kranyak J, et al. Repository corticotropin injection in patients with advanced symptomatic sarcoidosis: retrospective analysis of medical records. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2019;13:1753466619888127. doi:10.1177/1753466619888127.
References:
- Tumlin J, Galphin C, Santos R, Rovin B. Kidney Int Rep. 2017;2(5):924-932.
References:
- Nelson WW, Lima AF, Kranyak J, et al. Retrospective medical record review to describe use of repository corticotropin injection among patients with uveitis in the United States. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2019;35(3):182-188.
References:
- Wirta D, McLaurin E, Ousler G, Liu J, Kacmaz RO, Grieco J. Repository corticotropin injection (Acthar® Gel) for refractory severe noninfectious keratitis: efficacy and safety from a phase 4, multicenter, open-label study. Ophthalmol Ther. 2021;10(4):1077-1092.
- Data on File – Ref-04624. Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
- US Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Clinical outcome assessment review. 2016. Accessed January 19, 2021. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2016/208073Orig1s000MedR.pdf.
- Grubbs JR, Tolleson-Rinehart S, Huynh K, Davis RM. A review of quality of life measures in dry eye questionnaires. Cornea. 2014;33(2):215-218.
- Abetz L, Rajagopalan K, Mertzanis P, Begley C, Barnes R, Chalmers R; Impact of Dry Eye on Everyday Life (IDEEL) Study Group. Development and validation of the impact of dry eye on everyday life (IDEEL) questionnaire, a patient-reported outcomes (PRO) measure for the assessment of the burden of dry eye on patients. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2011;9:111.
- Fairchild CJ, Chalmers RL, Begley CG. Clinically important difference in dry eye: change in IDEEL-symptom bother. Optom Vis Sci. 2008;85(8):699-707.
References:
- Rahaghi FF, Sweiss NJ, Saketkoo LA, et al. Management of repository corticotrophin injection therapy for pulmonary sarcoidosis: a Delphi study. Eur Respir Rev. 2020;29(155):190147. doi:10.1183/16000617.0147-2019.
- Baughman RP, Scholand MB, Rahaghi FF. Clinical phenotyping: role in treatment decisions in sarcoidosis. Eur Respir Rev. 2020;29(155):190145. doi:10.1183/16000617.0145-2019.
- Acthar Gel (repository corticotropin injection) [prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: Mallinckrodt ARD LLC.
- Rahaghi FF, Baughman RP, Saketkoo LA, et al. Delphi consensus recommendations for a treatment algorithm in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Eur Respir Rev. 2020;29(155):190146. doi:10.1183/16000617.0146-2019.
References:
- Data as of 01/22. Data on File – Ref-05336. Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
References:
- Data on File – Ref-05118. Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
References:
- Data on File – Ref-05292. Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
References:
- Data on File – Ref-05291. Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
References:
- Data on File – Ref-04568. Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
- CellCept (mycophenolate mofetil) [prescribing information]. San Francisco, CA: Genentech USA, Inc.
References:
- Data on File – Ref-04990. Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
References:
- Madan A. Repository corticotropin injection in a patient presenting with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and optic neuritis: a case report. Int J Gen Med. 2015;8:119-124.
References:
- Fernandez AP, Gallop J, Polly S, Khanna U. Efficacy and safety of repository corticotropin injection for refractory cutaneous dermatomyositis: a prospective, open-label study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023 Nov 6. Epub ahead of print. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead595
- Anyanwu CO, Fiorentino DF, Chung L, et al. Validation of the Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI): characterizing disease severity and assessing responsiveness to clinical change. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173(4):969-974.
References:
- Anesi SD, Chang PY, Maleki A, et al. Treatment of noninfectious retinal vasculitis using subcutaneous repository corticotropin injection. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2021;16(2):219-233.
References:
- Anesi SD, Chang PY, Maleki A, et al. Effects of subcutaneous repository corticotropin gel injection on regulatory T cell population in noninfectious retinal vasculitis. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2023;31(3):556-565.
References:
- Hladunewich MA, Cattran D, Beck LH, et al. A pilot study to determine the dose and effectiveness of adrenocorticotrophic hormone (H.P. Acthar® Gel) in nephrotic syndrome due to idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2014;29(8):1570-1577.
- Acthar Gel (repository corticotropin injection) [prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: Mallinckrodt ARD LLC.
References:
- Wynn D, Goldstick L, Bauer W, et al. Results from a multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of repository corticotropin injection for multiple sclerosis relapse that did not adequately respond to corticosteroids. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022;28:364-371.
- Kurtzke JF. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology. 1983;33(11):1444-1452.
- Busner J, Targum SD. The clinical global impressions scale: applying a research tool in clinical practice. Psychiatry (Edgmont). 2007;4(7):28-37.
- Hobart J, Lamping D, Fitzpatrick R, Riazi A, Thompson A. The Multiple Sclerosis Impact Scale (MSIS-29): a new patient-based outcome measure. Brain. 2001;124(Pt 5):962-973.
- Kaplan J, Miller T, Baker M, Due B, Zhao E. A prospective observational registry of repository corticotropin injection (Acthar® Gel) for the treatment of multiple sclerosis relapse. Front Neurol. 2020;11:598496.
References:
- Data on File – Ref-07075. Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.
References:
- Data on File – Ref-07195. Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals.